The most characteristic manifestation of hypertension is an increase in pressure.
As a rule, increased pressure with hypertension can already be installed when examining the pulse.When you feel the impulse on the radial artery, a solid impulse (p. Durus) is determined, due to an increase in intra-arterial pressure and the tonic reduction of the walls of the artery.However, due to the fact that the light of the medium caliber arteries with hypertension decreases slightly, the filling of the pulse changes little.During the graphical recording of the pulse oscillations (on the sphigmogram), the pulse wave is low, rounded, has an excitement of lifting and descent (Tardus pulsus);The dicrotic wave is discreet.
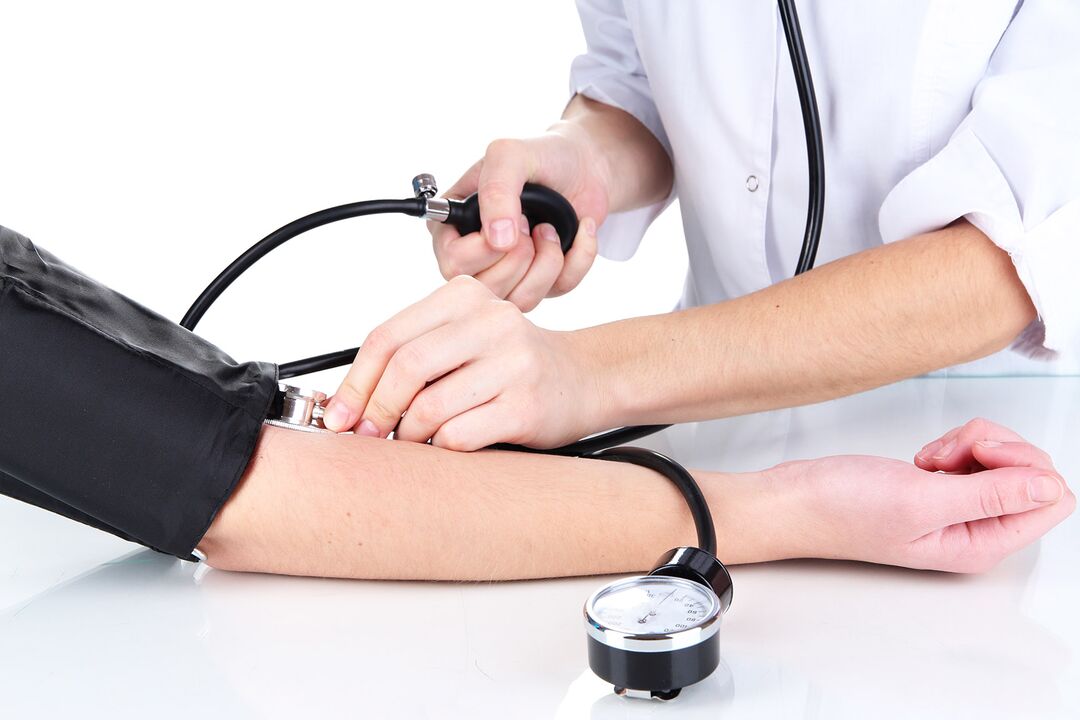
The study of blood pressure by the auscultative method is always the best way to simultaneously determine the systolic, diastolic and impulse pressure.With hypertension, the three values are generally increased.The seistolic is most significantly increased;Diastolic increases to a lesser extent.
If we compare the percentage of the increase in the magnitude of the systolic and diastolic pressure for hypertension compared to the average values of the two pressure in the standard, then the climb will be almost equal.So, if we take for a normal value for systolic pressure a number of 120 mm and for the diastolic pressure - 70 mm Hg. Art., Then at a blood pressure equal to 160 mm Hg. Art.(maximum) and 90 mm Hg. Art.(minimum), an increase compared to the standard compared to the two values will be almost the same (90 against 70 and 160 compared to 120).With an indicator of 180/100 mm Hg. Art.At first glance, it seems that systolic is increasingly increased than diastolic (180 against 120 and 100 against 70);If you compare yourself with normal ratios, the increase in percentage is almost equal.
Often in the initial period (stage I) of hypertension, there is an increase in systolic or diastolic pressure (often the first, less often the second).It perhaps depends on the initial level which has before the disease (each person individually).
The relationship between diastolic and systolic pressure affects:
- The degree of elasticity of the walls of the great arteries,
- Socratic power of the heart.
It is well known that a decrease in the elasticity of the arteries contributes to increasing the systolic pressure (in the most pronounced form, it is in the atherosclerosis of the central arteries).
With hypertension, changes in the elasticity of the walls of large vessels are observed, which is reflected in an increase in pulse pressure.Under the same conditions, when the heart begins to weaken, the amplitude becomes lower: the systolic pressure decreases, the diastolic leftovers have increased.
Already at the start of the disease, a tendency to put pressure is observed.The measurement of blood pressure shows that in some patients, its level does not go beyond the upper limit of the age standard, but obtained when the measurement of size is higher than the habit for a given person, while in others, it exceeds the upper limits of the age of age.Increased pressure with hypertension is observed under the influence of various effects - mental, emotional, reflex - and is maintained at an increased level from several minutes to several hours.
The first dimension generally gives higher numbers (random pressure) that the repeated measurements taken after 5-10-15 minutes.The difference between the quantity of random and basic pressure is indicated by "additional pressure";Its value in people with hypertension is much greater than in healthy people.The main pressure obtained in the conditions of the study of the main exchange is considered to be the main one (that is to say in bed, in the morning after sleep, on an empty stomach).The smallest value of the indicator after repeated measurements in the usual environment is conditionally called "almost the main pressure".
The "additional pressure" undoubtedly expresses the degree of mental (emotional) mental excitement or the patient's tension at the moment and the degree of excitability of his nervous, which regulates the blood pressure of the device.Experience shows that during the pregypertonic period in patients, the value of additional pressure is generally greater than in people who have not found a tendency to develop hypertension.
By comparing the degree of influence of certain nervous influences, it should be noted that the clearest stimulus is the word.Consequently, it will not be an exaggeration to say that the impact of the second signaling system in the greatest extent affects the increased pressure level for hypertension and in those who are predisposed to it.
Samples for increased pressure with hypertension
They tried to determine the inclination to hypertension by reflex irritations.In this regard, special attention has been paid to the SO-appeal cold sample.In studies after a short period of rest, the blood pressure is measured in a lying position, then the brush with the other hand is immersed in a temperature of 4 ° for a minute;At the time of immersion, then every 30 seconds, the level is measured until it rents.An increase in systolic pressure is greater than 20 mm Hg. Art., Diastolic of more than 15 mm Hg. Art.serves as an indicator of an increase in the reactivity of the presser.The faces that discovered it were called "hyperreactors", which did not find - "hyporeactors".Among healthy people, hyperreactors are 15%.
The cold sample received a contradictory assessment.In the pressing effect, with this sample, the conditions under which the sample is carried out play an important role.An pressing reaction to cold in a hot person, due to a reduced tone of their ships is lower than that of the same person in cooler external temperature conditions.The reflex reaction to cold depends on the usual temperature influences, on the profession, the living conditions.It is well known that people are used to the temperature factor.For hardened people, a cold test can be low and in people sensitive to cold, it can be strongly expressed.
The cold sample is based on the reflex reaction of the vasomotor center in response to thermal irritation (and partially of pain) suddenly on the periphery.The urgent reaction to the cold is weakening after taking alcohol, bromine, barbiturates.
Sometimes, responses to the cold sample are paradoxical: increased pressure in hypertension does not occur, and sometimes it even decreases.
It is interesting to compare this data with the results of determining blood pressure after the influence of heat.When you warm your hands in people with hypertension, it is often not a decrease, but an increase in blood pressure (a hand lowered in hot water does not blush, but pale).Therefore, cold and heat can sometimes cause the same pressing vasoconstrictor effect.
The temperature effects can hardly be used as a method to assess the responsiveness of the device which regulates increased pressure in hypertension, as they do not reflect the specifics of disorders that underlie hypertension.Vascular samples using pharmacological agents have been proposed.One of them is a sample with a glycerol trinitrate.After taking 2 drops of glycerol trinitrate (under the language), the pressure (systolic and diastolic) decreases significantly.The decrease is more pronounced in people with highly increased pressure in hypertension.Decrease particularly significantly with unstable blood pressure;Sometimes such a decrease is observed with persistent hypertension.In the late stages of hypertension (with the development of arteriolosclerotic changes in the kidneys), a nitroglycerin test gives a slight decrease in the hypertension indicator, which can be used to diagnose renal forms (or steps) of hypertensive conditions.
The same results (the depressant effect) gives a test with the inhalation of isoamilnitrite.Trinitrate glycerin, such as isoamilnitrite, acts mainly by central vascular devices, thus characterizing the increased excitability of these hypertension centers.
A sodium test was somewhat propagated.The person studied in bed gives an amyle of sodium 0.2 g every hour 3 times;The blood pressure is measured before the preparation of the medication and every half hour after having taken it (within 3 hours).The difference between the initial level and the smallest determines the value of the depressant effect.After taking the second powder, a dream generally occurs.As a rule, sodium friendly helps reduce blood pressure not only in the early hours, but also in the following days, sometimes even several days;The patient's well-being improves.However, such an effect is not always observed: some patients have medication intolerance.
Unlike a nitrite test, which causes greater drop in pressure, when sodium sodium is sodium, it gradually decreases.The degree of decrease in its intake is particularly significant at the start of the disease.At the end of the period, in the presence of arteriolosclerotic changes in the kidneys, the decrease is generally small or absent.
Given that the effect of barbiturates, without a doubt, is central, a sodium test with AMMAL is characterized by the state of the regulatory pressure of the instrument in the cortical and subcortical regions.When you use various doses of medication (small and large), it is possible to judge the phase conditions of vasopressor nerve centers by blood pressure (sometimes large and small doses give the same effect, or small doses have a depressive effect, more distinct as large doses).
In addition to samples based on the action of the depressant, there are many samples based on pressing action - with respiratory stop, inhalation of carbon dioxide, taking phenamine, but they are not without negative effects on the condition of the patients, although they probably do not determine the inclination of hypertension to its early stageSo-Called.
After discovering an inclination to a short -term increase in blood pressure in a particular person, you should not immediately diagnose hypertension, and even more to inform examination about it.Under favorable environmental conditions, instant reactions can go completely.
Increased pressure as a function of the hypertension stage
Increased pressure at the initial stage can only be periodically (transient phase).The more the patient's neuropsychiatric conditions, the most prolonged and the most frequent are increased pressure periods in hypertension and periods of the normal level of its shorter and rarer.Therapeutic measures, the compliance of the diet are very important.Under the influence of rest and treatment in the initial transitional phase of hypertension with a benign course, the indicator often decreases at a long period.
An increasingly obstinate inclination of increased pressure during hypertension and preservation of its pathological level indicates the subsequent development of the disease which passes at the second stage.In phase A of stage II, blood pressure is educated (labile phase).Its level can fluctuate in large limits.Under the influence of rest, it is reduced by a short period of time at a level close to normal, although it is not maintained at this level for a long time.Under the influence of treatment, however, a prolonged decrease in the indicator of the standard can be obtained.
During the day, blood pressure with hypertension can vary considerably.In the morning, it is generally lower than in the evening.After eating, it increases slightly, then gives a significant decrease.During night sleep, it decreases more sharply with hypertension than in the healthy.
As the disease progresses, blood pressure is more firmly set to a high level (phase B II, stable).Admittedly, at this stage, periods of decrease are sometimes observed.Sometimes remission occurs under the influence of prolonged therapy for quite a long time.However, this phase generally differs obstinate and high hypertension.The depressant tests at this stage indicate the functional nature of increased pressure in hypertension.
In stage III, blood pressure is generally resistant.Hypertension is supported by a number of factors, among which there is undoubtedly the participation of the renal.However, with a decrease in the excitability of vasopressor centers in brain vascular accidents or under the influence of heart failure (the occurrence of soil decompensation of the contractile function of a hypertrophied heart), a decrease in blood pressure is noted.Moderate heart failure is not much reflected in the indicator;Sometimes it even increases during this period (stagnation factor).
As for venous pressure in hypertension, it is generally within normal limits, only increases with heart failure.Admittedly, some patients can also be found at the early stage of the disease, several increased venous pressure values, which has even led to the "Center Venomotor" hypothesis, as a result of which the tone of venous walls increases (however, we are not able to judge the latter, because generally the interethnosis pressure is measured blood).The blood pressure in the capillaries is inaccessible to the definition.Capillaryoscopically in the nail bed, the narrowing of the arterial knees of the preapillars and the expansion of the venous knees are generally determined;Typical variability of the image of capillaries ("game" of them).















